A chatbot is an automated program that engages in conversation with users, simulating human interactions. They’re affordable, efficient, and bring undeniable advantages to various business facets, from marketing to sales and support.

Their primary roles include:
- Offering 24/7 and scalable service to multiple users simultaneously without requiring human intervention or supervision.
- Reducing the workload and pressure on the human staff, who can focus on more complex or urgent tasks or cases.
- Enhancing user satisfaction and loyalty by offering a fast, convenient, and personalized onboarding experience.
- Boosting user engagement and retention by providing relevant information, guidance, feedback, and incentives during the onboarding process.
- Collecting and analyzing user data and feedback, which can help optimize and improve the onboarding process and the product or service.
However, they have their limitations. While they can handle a wide range of customer inquiries and provide instant assistance, there are certain complex or nuanced situations where a human touch may be required.
How Does a Chatbot Work? The Simple Explanation
Imagine you have a friend who loves trivia. You ask them a question, and they instantly reply with an answer. Now, instead of your friend, picture a computer program doing this. That’s a chatbot! But how does it do its magic? Here’s a peek behind the curtain:
- You Ask Something: This is where you type or say something to the chatbot.
- Listening & Understanding: Just like when you chat with a friend, the chatbot needs to understand what you’re saying. Using a special tool called “Natural Language Processing” (NLP), the chatbot breaks down your words to figure out what you mean. It’s like decoding a puzzle!
- Finding the Answer: Once the chatbot understands you, it dives into its vast sea of information or rules to find the best response.
- Replying Back: The chatbot then sends you its answer. It could be a text, a link, a picture, or even an emoji!
- Learning & Improving: Some advanced chatbots learn from their conversations. So, if they made a mistake or found a better way to reply, they remember it for next time.
A Real-Life Example:
Imagine texting a pizza place’s chatbot:
- You: “I’d like a large pepperoni pizza, please.”
- Chatbot: Breaks this down to: [Order] + [Size: Large] + [Type: Pepperoni Pizza]
- Chatbot: Responds, “Sure! Your large pepperoni pizza will be ready in 20 minutes.”
And there you have it! That’s how chatbots work, from the moment you say “hello” to getting the info or help you need.
Technically, a chatbot is a computer program that uses text or voice interactions to make it seem like you are talking to a person. It can be used to do many different things, like answer frequently asked questions, help customers, and even buy things.
They can be used with websites, messaging apps, and voice assistants to make communication with users easier and more efficient.
The term “chatbot” is a combination of two words: “chat” and “bot.”
The “chat” aspect refers to the conversational nature of the interaction, while the “bot” aspect refers to the fact that the program is automated.
Chatbots are designed to be able to understand and respond to user input, which can be in the form of text or voice.
Chatbots have been around for decades, but recent advancements in natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning have made them more sophisticated and effective in their interactions with users.
NLP is an area of artificial intelligence (AI) that lets computers understand human language. It is one of the most important technologies used to build chatbots. Machine learning is a method of teaching computers to learn from data, which allows chatbots to improve their understanding of user inputs over time.
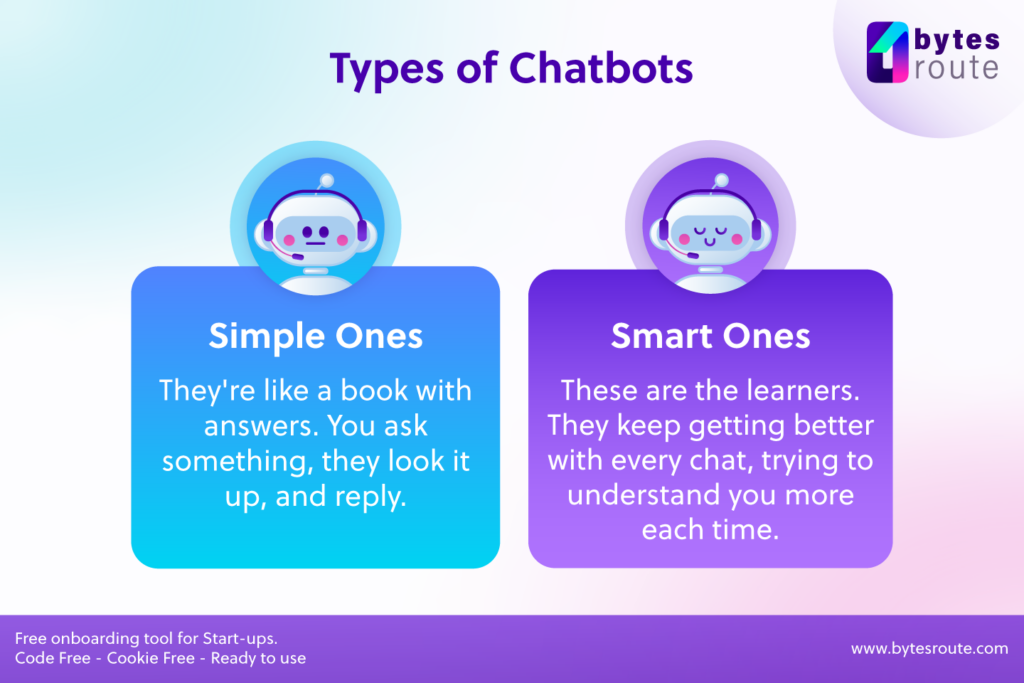
Types of chatbots
There are two main types of chatbots:
- Rule-based chatbots and
- Self-learning chatbots
Rule-based chatbots are set up with a set of rules that tell them how to respond to different things.
AI chatbots, which are chatbots that can learn on their own, use machine learning algorithms to get better at understanding what users say and changing their responses to match.
To make a chatbot, you may need to know how to code, but many platforms have pre-built templates and drag-and-drop interfaces that make it easier for people who don’t know how to code or don’t want to learn.
What are chatbots used for?
Chatbots can be used for a variety of tasks,
- answering frequently asked questions,
- providing customer service,
- and even making purchases.
A chatbot can be useful for a number of things for companies, such as:
- Lead generation
A chatbot can be used to talk to potential customers and find out what their needs and interests are. The sales team can then use this information to find new leads.
The information collected can be used to qualify leads and figure out which ones are most likely to turn into paying customers. This way, it fulfills a successful customer adoption process, to your own business benefit.
Most of the time, the chatbot is used to get contact information from potential customers, such as their email addresses and phone numbers. This information can then be used to follow up with leads and move them further down the sales funnel.
One of the most common uses of a chatbot is to send targeted content to leads based on their interests and actions, which is a real help in automating the lead nurturing process.
- Providing personalized access to helpful resources: whitepapers, ebooks, and webinars to educate leads and help them make a purchasing decision.
- Sending targeted follow-up messages reminding them of their interest in the product or service and encouraging them to take the next step.
- Also,it can help to schedule appointments with potential customers, allowing sales reps to focus on more high-value activities.
- Customer service
The most valuable contribution of a chatbot is that it can be used to provide 24/7 customer support.
It can also be trained to answer common questions and troubleshoot issues. All in multiple languages, covering assistance for customers from all over the world.
Helping with self-service: Customers who prefer to find their own answers to their questions on their own can get help from a chatbot.
It turned out that using a chatbot to gather customer feedback about their experience with customer support is more effective because providing feedback is frequently simpler when a non-human is assisting the process.
- Employee engagement:
A chatbot can be used to answer questions from employees, tell them about policies and benefits, and even do HR-related tasks.
Even if the human factor is excluded, a chatbot can bring some important benefits to employee productivity and engagement:
- quick access to information they need, improving their productivity and engagement.
- automate repetitive HR tasks, such as updating employee information or scheduling meetings, freeing up employees to focus on more important tasks.
- improve communication between employees and HR staff, making it easier for employees to get the assistance they need.
- provide personalized support based on the information it has gathered from the employee.
- provide employees with self-service options, allowing them to access information, request time off, or update their information without having to go through HR.
- provide employees with instant feedback and recognition, enhancing employee engagement and motivation
- gather employee feedback and suggestions, which can be used to improve the work environment and employee satisfaction.
Chatbots can be used to automate tasks that people do over and over again. This cuts down on the need for human labor and saves the company money.
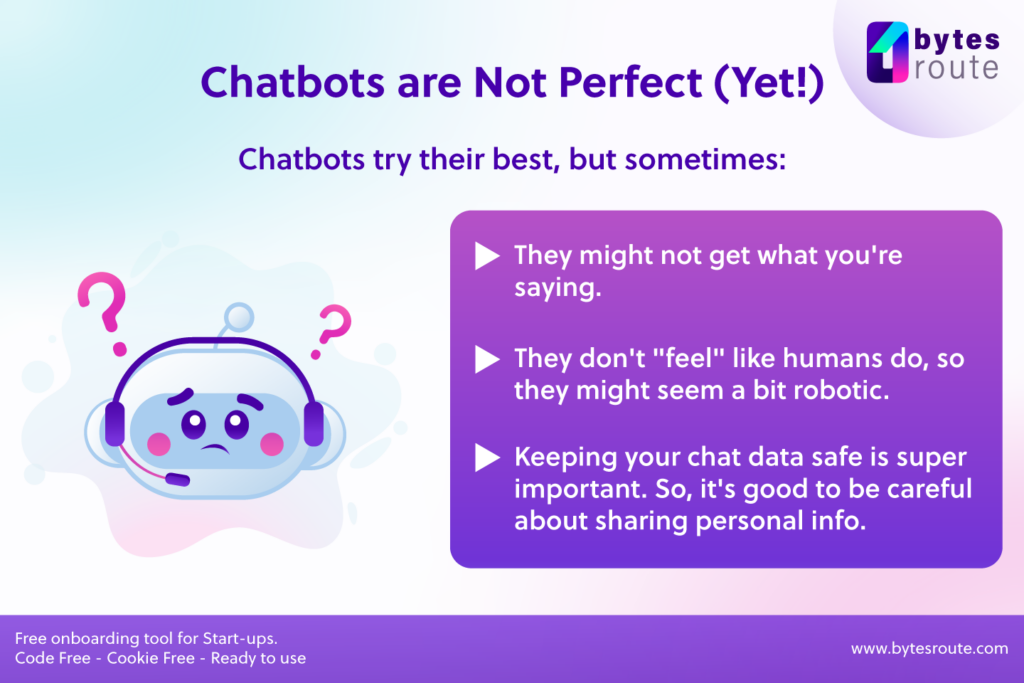
Disadvantages and limitations of using chatbots
We went through various use cases for chatbots, each with lots of advantages. But there are some concerns and limitations to using chatbots, too:
- Limited understanding, since chatbots may have difficulty understanding complex or nuanced questions or requests, resulting in frustration for the customer or employee.
- Lack of empathy: chatbots do not have the ability to empathize with customers or employees, which can result in a poor customer or employee experience.
- Limited personalization: chatbots may not be able to provide the same level of personalization as humans, which can result in a less effective customer or employee experience.
- Privacy concerns: by collecting and storing sensitive personal information, which can raise privacy concerns and require organizations to implement additional security measures to protect that data.
- Low complexity: chatbots may not be able to handle complex or high-value tasks, requiring customers or employees to speak with a human representative.
- Maintenance requirements: Chatbots must be checked and updated on a regular basis to ensure that they are providing accurate and useful information.
- Limited ability to improve: The performance of a chatbot is limited by its underlying algorithms, and it may not be able to improve its performance over time the way a human can.
In short, a chatbot is a computer program that uses text or voice interactions to make it seem like it is talking to a real person.
A chatbot can have various roles and places within a digital onboarding process, such as:
- Providing information and guidance to the user about the product or service, its features, benefits, and requirements.
- Collecting and validating the user’s data, such as name, email, phone number, preferences, etc.
- Answering the user’s questions and resolving their doubts or issues.
- Recommending the best options or solutions for the user’s needs and goals.
- Engaging and motivating the user to complete the onboarding process and to use the product or service.
- Soliciting feedback and ratings from the user about their experience and satisfaction.
A chatbot can help improve the digital onboarding process by making it more interactive, personalized, convenient, and efficient. A chatbot can also help reduce the costs and resources associated with human support and increase the conversion and retention rates of users.