What is Process Mapping, and why is it important?
Process mapping is a technique for visually representing the steps of a process or system. Its purpose is to break down the process into smaller, more manageable parts that are easier to understand.
The process mapping exercise involves documenting, analyzing, and improving the process in order to maximize its efficiency. This is done by constructing a flowchart or diagram that highlights the inputs, activities, decisions, and outputs that make up the process.
Process mapping allows users to immediately discover any inefficiencies, redundancies, or other issues that are disrupting the process. As a result, the process is optimized and productivity is increased.
Process mapping can be applied in different contexts such as business process management, project management, quality management, and software development. In each of these contexts, the objective is the same – to streamline the process and improve efficiency.
Types of process maps
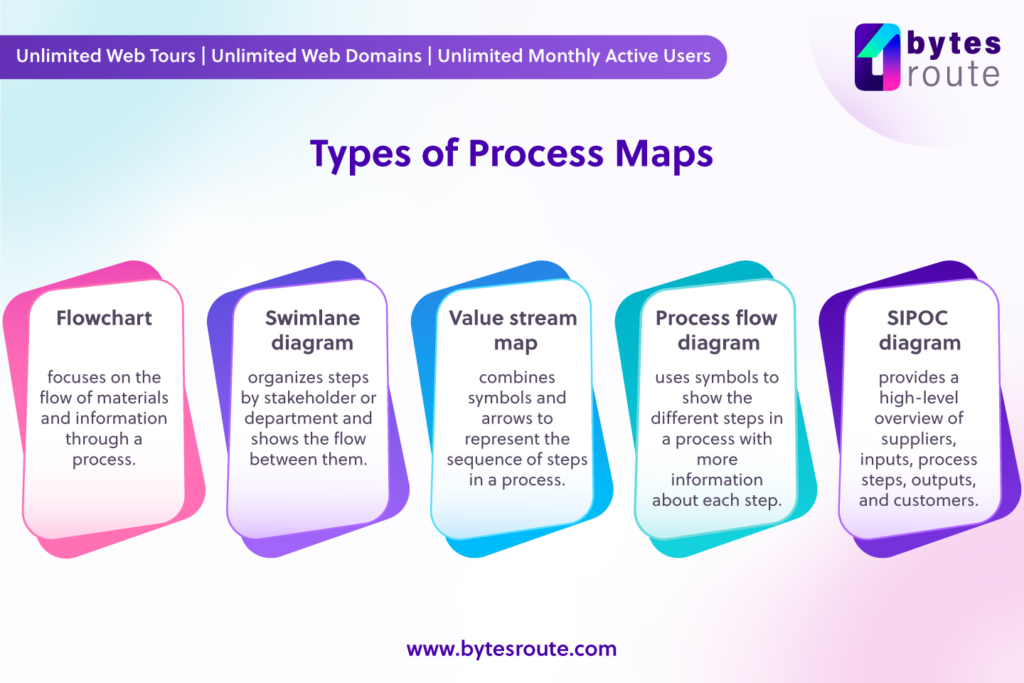
There are various sorts of process maps, each with its own function and amount of detail. Below are some of the most frequent forms of process maps:
- Flowchart: A flowchart is a graphic that combines symbols and arrows to represent the sequence of steps in a process. It is the most popular sort of process map and is useful for understanding the general flow of a process.
- Swimlane diagram: A swimlane diagram is a form of flowchart that depicts the steps of a process arranged by different stakeholders or departments. Each swimlane symbolizes a distinct group involved in the process, and the diagram illustrates the flow of the process between the various groups.
- Value stream map: A value stream map is a sort of process map that focuses on the flow of materials and information through a process. It is used to discover areas of waste and inefficiency in the process and to improve the overall flow of value.
- Process flow diagram: A process flow diagram is a type of process map that uses symbols to show the different steps in a process. It is similar to a flowchart but has more information about each step.
- SIPOC diagram: A SIPOC (Supply, Input, Process, Output, Customer) diagram is a sort of process map that provides a high-level overview of a process. It outlines the essential inputs, outputs, and stakeholders involved in the process.
Each type of process map is beneficial for different purposes, and the choice of which one to employ relies on the level of detail necessary and the objective of the process mapping activity.
Benefits of process mapping
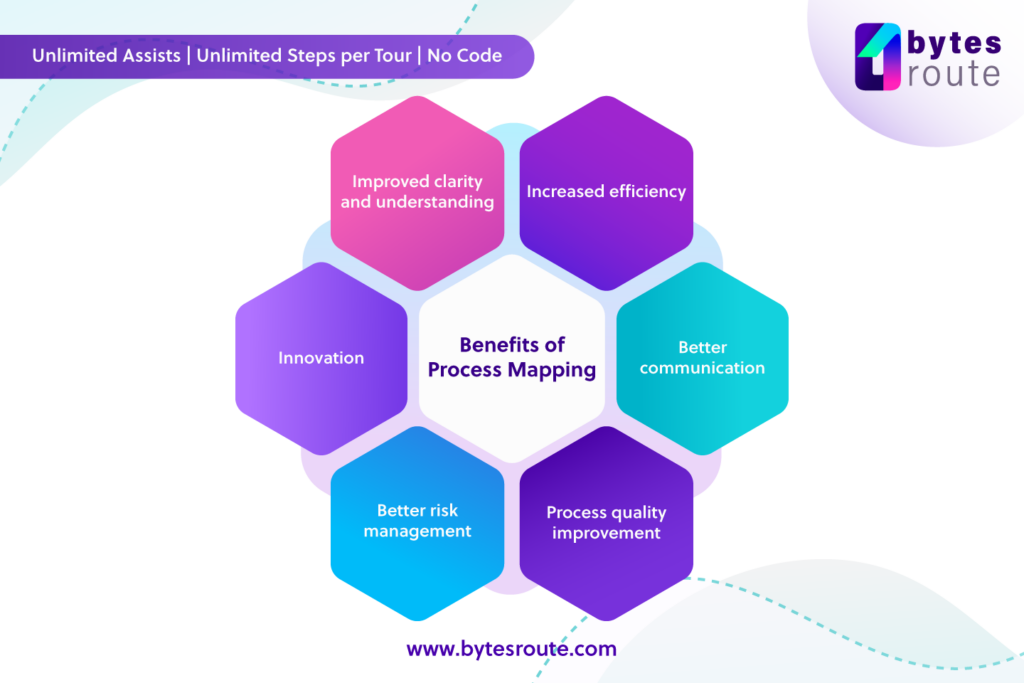
Process mapping has various advantages for businesses of all sorts and sectors.
One of the major advantages of process mapping is the ability to discover opportunities for improvement. Businesses can identify inefficiencies, redundancies, and bottlenecks by breaking down a process into its component elements and visualizing each step. This knowledge enables companies to implement focused adjustments that can have a major impact on productivity, quality, and customer happiness.
Another benefit of process mapping is that it helps to maintain process consistency and standardization. Businesses can reduce the risk of errors and inconsistencies by developing a shared understanding of a process, resulting in higher-quality output. This is especially crucial in highly regulated industries like healthcare or banking, where even little mistakes can have major implications.
Finally, process mapping can assist firms increase team communication and collaboration. Teams can work more effectively together and find places where they can support one another by providing a visual representation of a process. This can lead to better teamwork, higher morale, and ultimately better results.
Ultimately, the advantages of process mapping are numerous, making it a must-have tool for companies trying to streamline their operations and achieve long-term success.
Steps for creating a process map
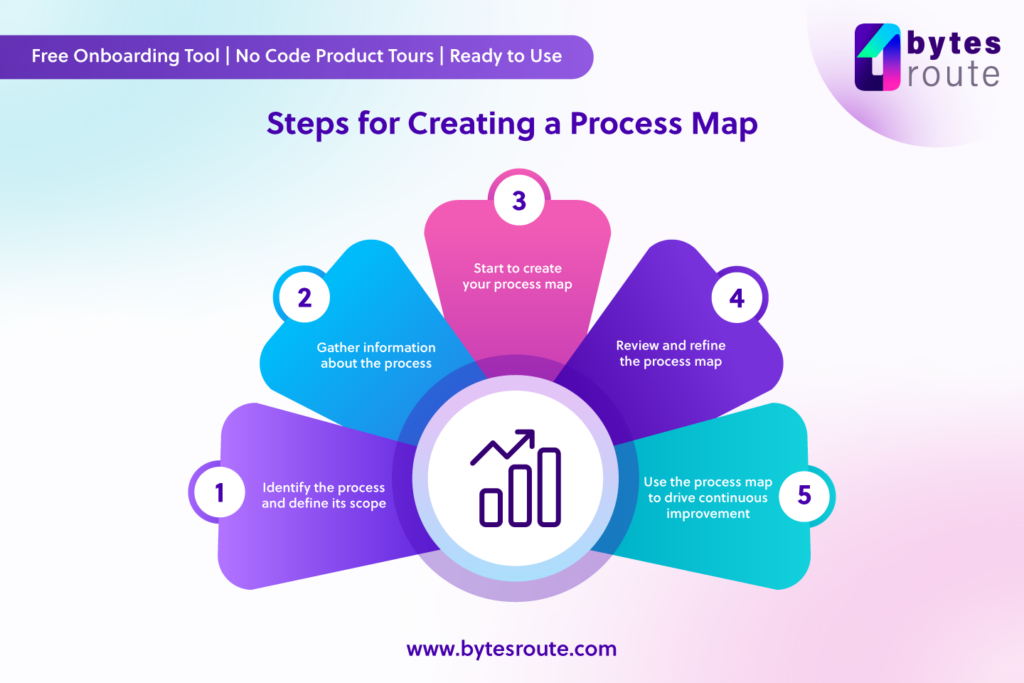
There are several steps involved in creating a process map. Firstly, it’s important to identify the process that you want to map out and define its scope. This involves identifying the start and end points of the process, as well as any sub-processes that are involved.
Next, you’ll need to gather information about the process. This can include speaking with employees who are part of the process, reviewing documentation or standard operating procedures, and observing the process in action.
Once you have this information, you can start to create your process map. This typically implies using a visual tool such as a flowchart or swimlane diagram to map out the process step-by-step. It’s important to be clear and concise in your descriptions of each step and to include any relevant information such as inputs, outputs, or decision points.
After creating the initial process map, it’s important to review and refine it. To do this, share the map with other stakeholders to gather feedback, identify areas for improvement, and make any necessary adjustments.
Finally, it’s key to use the process map to drive continuous improvement. For instance, regularly reviewing and updating the process map as the process changes or as new information becomes available. By continuously refining the process map, businesses can ensure that their processes remain optimized and efficient over time.
Best practices for process mapping
To begin, it is essential to clearly identify the scope of the process mapping exercise. This ensures that all participants are on the same page with the exercise’s aims and objectives, which can help to prevent scope creep.
Furthermore, we need to include employees who are involved in the process being mapped. This not only ensures that the map accurately reflects the actual process but also helps to build employee buy-in and engagement. They are the most knowledgeable about the process and can provide helpful insights.
Next, it is vital to have a uniform and standardized approach to process mapping. This can include adopting a standardized set of symbols, vocabulary, or software to ensure that the process map is simple to comprehend and consistent across processes. Its consistency makes training new personnel and comparing different processes easier.
Fourth, it is a must to review and update the process map on a frequent basis to ensure that it is correct and reflects any changes to the process. An out-of-date process map can cause confusion and errors.
Ultimately, use the process map to drive continual improvement. This involves examining the process map on a regular basis to identify areas for improvement and taking action to address them. This can aid in the optimization of the process, as well as the improvement of quality and efficiency through time.